Key Takeaways
- Diabetes is a chronic disease that's common among older adults, affecting an estimated 33% of people aged 65 and older.
- Diabetes symptoms in older adults can range from mild to severe. They include excessive thirst and urination, blurry vision, and fatigue.
- Diabetes symptoms in older adults can range from mild to severe. They include excessive thirst and urination, blurry vision, and fatigue.
Symptoms of diabetes in older adults
- Increased thirst and urination
- Excessive fatigue
- Wounds that heal more slowly
- Dizziness and/or fainting
- Headaches
- Tingling sensations in hands and feet
- Blurry vision
- Gum problems
- Increased appetite
- Dry mouth
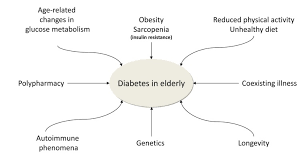
The aging population is growing worldwide and the proportion of people above 60 years old accounts for 15% of the whole population which is estimated to 7.5 billion.
Diabetes in elderly includes two groups: “survivors” of young or middle age onset of diabetes, and incident diabetes in older age or type 2 DM.
Type 1 DM is exceptional in elderly as auto immune diseases affect young populations. So old people with type 1 DM are practically at the end stage of their disease and are multi complicated.
Most people over than 60 years old suffer from type 2 DM due to insulin resistance. However, insulin secretion may be severely reduced at the end stage of type 2 DM.
Complications, and management of DM in elderly vary according to hyperglycemia duration and personal background. Some old people do not have any complication and are easy to manage; others are multi complicated and have additional severe diseases difficult to treat.
In old people, Vitamin D deficiency seems to be an additional factor, as some authors think Vitamin D deficiency is a link between osteoporosis, insulin resistance, obesity, diabetes and cognitive impairment, especially Alzheimer disease.
Signs of advanced dehydration such as dry mouth, dry eyes, and dry skin should attract the attention, but usually, old people with DM are diagnosed at the late stage of dehydration with confusion, agitation, delirium, or hyperosmolar coma.
On another hand, high blood pressure and dyslipidemia, cerebrovascular, and chronic pulmonary diseases generally coexist with DM in elderly, which increases the risk of poly medication.
Old people usually have severe osteoporosis due to vitamin deficiencies. Under nutrition due to isolation, depression, dental and/or socioeconomic problems contribute to bone demineralization too.
Vitamin D deficiency is one of the most frequent deficiencies in the elderly. It promotes diabetes through insulin resistance and insulin deficiency. It also predisposes to other metabolic, cardiovascular, and cancerous diseases.
Furthermore, Vitamin D deficiency is a strong factor for proximal muscle weakness, falls, and fractures. Old people are particularly at risk for low Vitamin D levels.
Solar exposure is usually limited because of less outdoor activity and diet is less varied with a lower natural Vitamin D content. The cutaneous production of Vitamin D decreases with age because of skin changes, with a reduced amount of Vitamin D precursors
Dizziness and orthostatic hypotension are responsible for old people falls. A strong decline in skeletal muscle tissue due to hormonal imbalance and body composition in elderly is one of the most important causes of loss of independence in old and frail people.
Muscles weakness obliges old people to use a cane or a wheel chair and exaggerates osteoporosis, which put old people at a high-risk of frequent falls and high incidence of hip, spine, and distal forearm fractures.